Hasan Almassri
Detection of Repetitive Parking Lot Boundaries for Near Range Camera Systems
Duration of the Thesis: 6 months
Completion: November 2016
Supervisor: Dipl.-Ing. Manuel Tranzer (Robert Bosch GmbH)
Examiner: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Norbert Haala
Introduction
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), in these days have a great interest from the academic researchers as well as the automotive industry. One of driver assistance systems is the video camera system. One of video camera based technologies is parking assistance system. Parking assistance systems provide useful assistance that allows the car to drive in and out of parking lots without any external support by using various sensors to detect objects and parking lot boundaries around the car. One of the challenges which rises in these days, that a robust detection algorithms are needed, which work perfectly in parking lots boundaries that are marked using repetitive cobblestones with different colors at any period time of day under all weather conditions.
Motivation
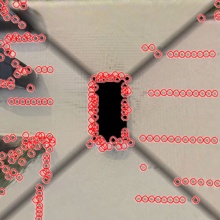
Dealing with repetitive parking lot boundaries where each type can have different boundary colour and shape as shown in figure 1, such patterns are often difficult to detect. The difficulty stems mainly from the problem of intensity image, colour of the boundaries and the shape of the cobblestones. Therefore, an algorithm is developed in this thesis, is required to detect the repetitive parking lot boundaries which are under a difficult environment such as rainy weather, sunny day with shadows in the ground and so on.
Implementation:
The proposed algorithm is based on a supervised classification. Figure 2 shows the flow chart for detecting the repetitive parking lot boundaries. Training dataset is used to compute the kernel parameters and to train the classifier. The feature vector of the input image will be calculated based on the selected features. By using these feature vectors with the classifier, the repetitive parking lot boundaries can be detected.
Testing:
Conclusion:
The main aim of this thesis was to examine the ability of support vector machine to detect and classify the repetitive parking lot boundaries regardless of their colors under various conditions. The experimental results show that this study have achieved its aim and it have approved that it is suitable for detecting the repetitive parking lot boundaries under different types of the boundaries as well as under different weather conditions.
Ansprechpartner

Norbert Haala
apl. Prof. Dr.-Ing.Stellvertretender Institutsleiter